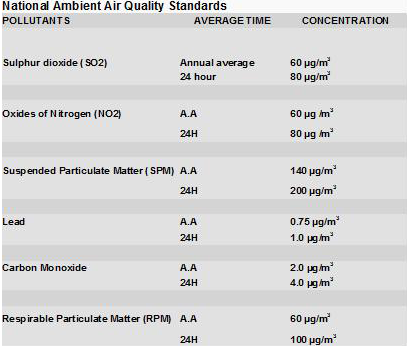
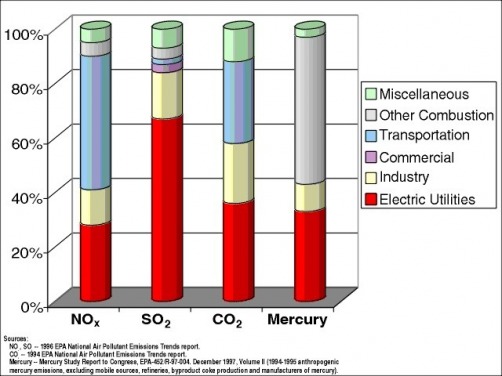
Pollutants

Pollutants can be classified as either
1. PRIMARY POLLUTANTS- There are many substances in the air which may impair the health of plants and animals(including humans), or reduce visibility . These arise both from natural processes and human activity. Substances not naturally found in the air or at greater concentration of different locations from usual are referred to as pollutants.These are substances directly emitted from a process, such as ash from a Volcanic eruption, the Carbon Monoxide gas from a Motor vehicle exhaust or Sulphur dioxide from factories.
2.SECONDARY POLLUTANTS - These are not emitted directly. Rather, they form in the air when primary pollutants reacts or interact. An important example of a secondary pollutant is Ground Level Ozone- one of the many secondary pollutants that make up photochemical smog.
Major contributors to air pollution are -
Primary pollutants include:
1. Sulfur oxides (SOx) -Especially sulfur dioxide are emitted from burning of coal and oil.
2. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) -Especially nitrogen dioxide are emitted from high temperature combustion. Can be seen as the brown haze dome above or plume downwind of cities.
3. Carbon monoxide-Is colourless, odourless, non-irritating but very poisonous gas. It is a product by incomplete combustion of fuel such as natural gas, coal or wood. Vehicular exhaust is a major source of carbon monoxide.
4. Carbon dioxide (CO2) -A greenhouse gas emitted from combustion.
5. Volatile organic compounds (VOC) -Such as hydrocarbon fuel vapors and solvents.
6. Particulate matter (PM) - Measured as smoke and dust. PM10 is the fraction of suspended particles 10 micrometers in diameter and smaller that will enter the nasal cavity. PM2.5 has a maximum particle size of 2.5 µm and will enter the bronchi and lungs.
7.Toxic metals- Such as lead, cadmium and copper.
8. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) -Harmful to the ozone layer emitted from products currently banned from use.
9.Ammonia (NH3) -Emitted from agricultural processes.
10. Odours- Such as from garbage, sewage, and industrial processes
11. Radioactive pollutants-Produced by nuclear explosions, war explosives, and natural processes such as the radioactive decay of radon.
Secondary pollutants include:
1. Particulate matter-Formed from gaseous primary pollutants and compounds in photochemical smog, such as nitrogen dioxide.
2. Ground level ozone (O3) -Formed from NOx and VOCs.
3. Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) -Similarly formed from NOx and VOCs.
Minor air pollutants include:
A large number of minor hazardous air pollutants. Some of these are regulated in USA under the Clean Air Act and in Europe under the Air Framework Directive.
A variety of persistent organic pollutants, which can attach to particulate matter.